Edge-LLMs in the 6G Era: A practical blueprint for private, ultra-low-latency AI using LoRA adapters, federated fine-tuning, and secure enclaves at the edge
Concrete blueprint for private, ultra-low-latency Edge-LLMs using LoRA, federated fine-tuning, and TEEs — tuned for 6G edge deployments.
Edge-LLMs in the 6G Era: A practical blueprint for private, ultra-low-latency AI using LoRA adapters, federated fine-tuning, and secure enclaves at the edge
This post gives engineers a hands-on blueprint for building private, ultra-low-latency Edge-LLMs optimized for 6G deployments. We’ll combine three practical levers you can implement today: lightweight LoRA adapters, federated fine-tuning for private personalization, and trusted execution environments (TEEs) to protect models and data at the edge. Expect architecture diagrams, deployment steps, and at least one executable-oriented code pattern you can adapt.
Why Edge-LLMs for 6G
6G promises sub-millisecond latencies, massive device densities, and sliceable network capabilities. That unlocks scenarios where large-language models must respond near-instantly, offline or with intermittent connectivity, and comply with strict privacy rules.
Centralized inference can’t satisfy these constraints: round-trip latency plus jitter, data residency rules, and network cost become blockers. Pushing models to the edge solves latency and privacy but introduces resource limits and attack surface concerns. The practical answer is a hybrid architecture that uses small-footprint inference combined with adapter-based personalization and privacy-preserving federated updates.
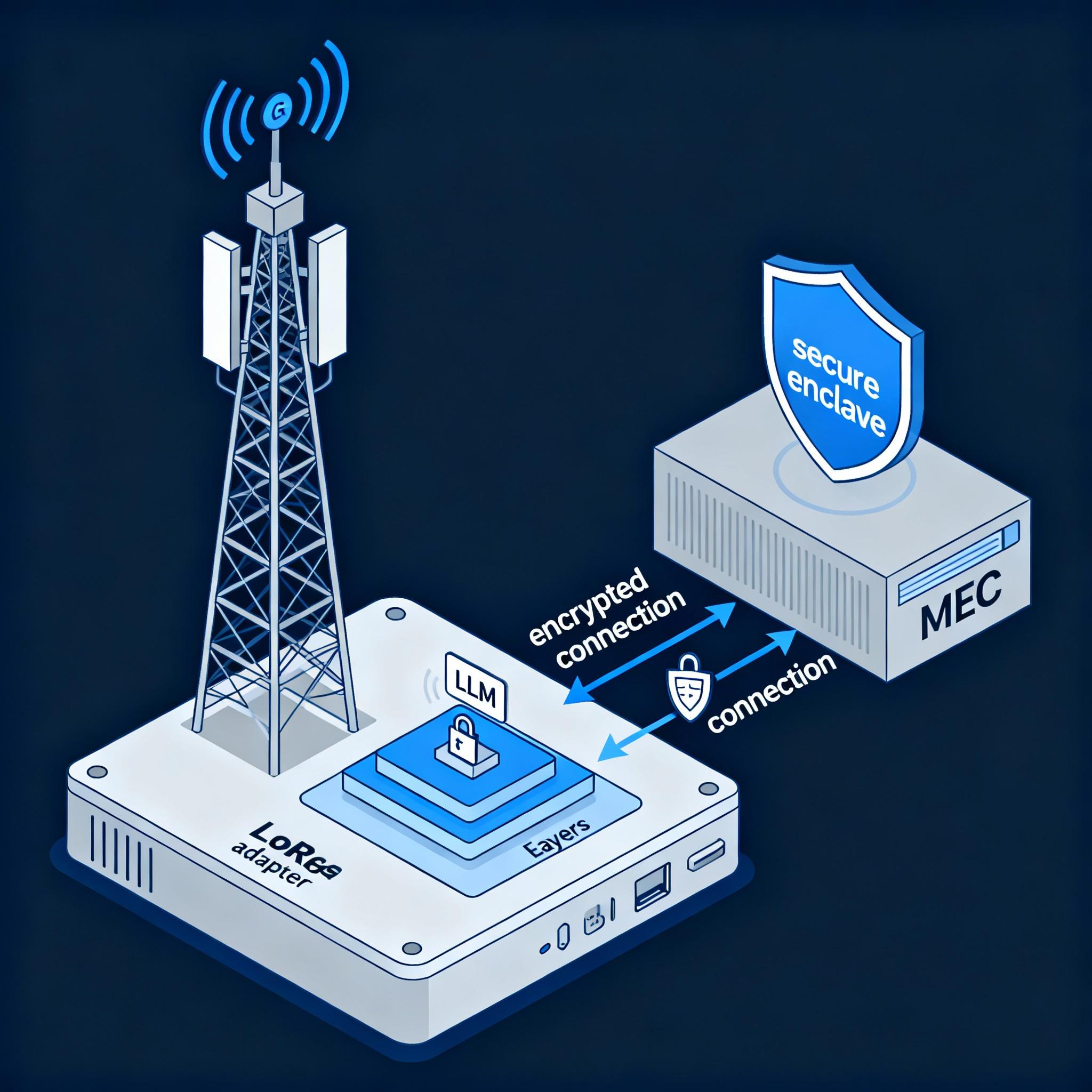
High-level architecture
- Edge device: constrained compute (ARM/NPU), runs quantized base model + LoRA adapters inside a TEE.
- Edge cluster / MEC: aggregation and model orchestration, secure enclave for federated aggregation.
- Cloud control plane: model hosting for base models, certificate management, and monitoring.
Key flows:
- Device boots a quantized LLM and loads signed LoRA adapter into the TEE.
- Inference runs locally — sub-10ms for optimized prompts on 6G links and on-device hardware.
- Periodically, local training updates adapter weights using private data; updates are encrypted and federated to the MEC.
- MEC aggregates encrypted updates inside a TEE, produces a new adapter version, signs and distributes it.
Component breakdown
Quantized base model
Start with a compact base model already quantized to 4- or 8-bit. The base model remains read-only; privacy-sensitive personalization stays in adapters.
Why quantize: power and memory are the biggest constraints at the edge. Use weight-only quantization and per-channel scales for best trade-offs.
LoRA adapters for personalization
LoRA (low-rank adapters) injects small, trainable low-rank matrices into transformer layers. Benefits:
- Tiny footprint: adapters are megabytes, not gigabytes.
- Fast on-device fine-tuning: only adapter parameters update.
- Model-agnostic: you can attach adapters to any frozen backbone.
Adapter lifecycle:
- Provision signed initial adapter from cloud.
- On-device fine-tune adapter with local data and privacy policies.
- Export encrypted gradients for federated aggregation.
Federated fine-tuning
Federated learning keeps raw data on device. Each client computes gradients or model-deltas and sends encrypted, optionally differentially private, updates to the aggregator.
Design choices:
- Communication pattern: asynchronous rounds work best for intermittent connectivity.
- Compression: send sparse or quantized deltas to reduce uplink.
- Privacy: use secure aggregation + differential privacy noise calibrated to adapter size.
Trusted execution environments (TEEs)
TEEs (Intel SGX, ARM TrustZone, or hardware-backed secure enclaves on NPUs) protect model secrets and handle secure aggregation. Use TEEs to:
- Store encrypted base model keys.
- Run inference and adapter loading with attestation.
- Aggregate encrypted updates securely at the MEC.
Combine TEEs with attestation APIs to prove to the cloud that the aggregator executed in a protected boundary.
Networking and 6G considerations
6G gives you deterministic slices and edge-native compute. For implementation:
- Use network slicing to prioritize inference traffic.
- Place MEC servers in slices that enforce low-latency SLAs.
- Leverage on-path compute for model distribution during low-traffic windows.
Plan for graceful degradation: when connectivity is lost, devices continue local inference and queue adapter updates.
Deployment blueprint — step-by-step
- Select base model and quantization strategy (4/8-bit). Keep the base model frozen on-device.
- Implement LoRA adapter injection points matching your transformer implementation.
- Boot a minimal runtime that runs the quantized model and exposes a safe API inside the TEE.
- Create a local fine-tuner that updates only adapter weights using a small optimizer (e.g., AdamW with low LR).
- Add an encrypted update pipeline with secure aggregation on the MEC, attested via TEE.
- Monitor model drift and manage adapter lifecycle from the cloud control plane.
Practical code pattern: on-device LoRA fine-tune and encrypted upload
The snippet below shows the core loop in pseudo-Python. It’s intentionally compact — adapt to your runtime and framework.
# load quantized backbone (frozen) and attach LoRA adapter
model = load_quantized_backbone('backbone.q4')
adapter = init_lora_adapter(rank=4, layers=12)
model.attach_adapter(adapter)
# on-device fine-tune loop (runs inside TEE)
for epoch in range(local_epochs):
for batch in local_data_loader():
preds = model.forward(batch.input)
loss = compute_loss(preds, batch.target)
adapter.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
clip_and_quantize_grads(adapter)
adapter.step(optimizer)
# compute delta, encrypt, sign, and upload
delta = adapter.compute_delta() # small tensor set
compressed = compress(delta) # e.g., top-k or quantized
encrypted = tpm_encrypt(compressed)
upload(encrypted, meta=attestation())
Notes:
- Run this loop inside the device’s TEE to keep raw gradients private.
- Use lightweight optimizers and small batch sizes to fit memory.
- Compress deltas aggressively: top-k, signSGD, or quantization.
Federated aggregation pattern
At the MEC, aggregation must be secure and auditable. Use a TEE-backed aggregator to decrypt and average updates.
# inside MEC enclave
collected = wait_for_encrypted_updates(timeout=60)
decrypted = [tpm_decrypt(u) for u in collected]
aggregated = secure_average(decrypted)
new_adapter = apply_delta(global_adapter, aggregated)
signed = sign(new_adapter)
publish_to_devices(signed)
Consider weighted averaging by client trust score and data quality. Add clipping to defend against poisoned clients.
Security checklist
- Enforce attestation for device and MEC TEEs.
- Store keys in hardware-backed keystores; never export private keys.
- Use secure aggregation to prevent the server from seeing individual deltas.
- Add DP noise at the client when regulatory requirements demand stronger guarantees.
- Validate adapter signatures before loading into the model runtime.
Performance tuning and cost trade-offs
- Adapter rank: rank 4–16 is a practical sweet spot; higher rank improves personalization at a cost.
- Quantization: 4-bit gives big RAM wins but needs careful calibration; 8-bit is safer.
- Update frequency: tune rounds based on user behavior—too frequent harms battery; too rare yields stale personalization.
- Compression: targeted top-k (e.g., k = 1% of params) reduces uplink dramatically while preserving signal.
Always measure: end-to-end latency, energy per inference, and overall user-perceived responsiveness.
Operational considerations
- Device lifecycle: implement a revocation and adapter rollback mechanism for compromised devices.
- Monitoring: telemetry must be privacy-preserving; rely on aggregated signals and TEEs for integrity.
- Versioning: maintain backward compatibility between adapter formats and backend aggregators.
Example checklist — ready-to-deploy
- Select and quantize backbone (4/8-bit) and validate inference latency on target hardware.
- Implement LoRA adapter integration and verify adapter rollback works.
- Build on-device fine-tuner that runs inside a TEE and uses small-batch updates.
- Implement encrypted, compressed update pipeline with secure aggregation on MEC.
- Add attestation hooks and cloud control plane for signing and distributing adapters.
- Set monitoring, clipping, and poisoning defenses at the aggregator.
Summary
Edge-LLMs in the 6G era are practical and necessary for ultra-low-latency, privacy-sensitive applications. Combine a quantized backbone with tiny LoRA adapters to enable on-device personalization, use federated updates with compression and DP for private model improvement, and secure everything with TEEs and attestation. This blueprint gives you a modular path: pick your quantization, attach adapters, protect with TEEs, and orchestrate federated aggregation at the MEC. Start with a minimal prototype: a frozen quantized model, a rank-4 adapter, and a TEE-backed training loop. Iterate on adapter rank, compression, and aggregation policies until you hit your latency and privacy targets.
Checklist:
- Prototype quantized backbone inference on target edge hardware.
- Integrate LoRA adapters and test local fine-tuning inside a TEE.
- Implement encrypted, compressed update upload and TEE-based aggregation.
- Add attestation, signing, and device revocation flows.
- Validate latency, energy, and privacy metrics in a field trial.
Edge-LLMs don’t require waiting for perfect networks. With LoRA, federated fine-tuning, and secure enclaves, you can build private, low-latency AI that fits the constraints and opportunities of the 6G edge.